McAfee conducted a study on cyber attacks on cloud services to determine if there has been an increase in attacks since the COVID-19 pandemic. The results are staggering, exposing a 630% rise in cyber attacks on cloud services since January 2020. With an increase of 50% in the use of cloud services, and a 600% increase in collaboration services, this discovery is troubling to say the least.
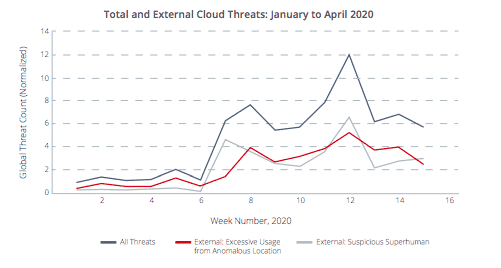 *McAfee Cloud Adoption and Risk Report
*McAfee Cloud Adoption and Risk Report
Is your organization secure?
Find out now with our HIPAA compliance checklist.
Cyber Attacks on Cloud Services and Healthcare
With the expansion of telehealth services, many healthcare providers have turned to cloud services to facilitate telehealth sessions. Due to the increase in cloud service use in healthcare amid the COVID-19 crisis, healthcare breaches have also increased. McAfee found that in the first quarter of 2020, the healthcare industry was the second most targeted industry for cyber attacks on cloud services, with 198 million malicious IPs detected.
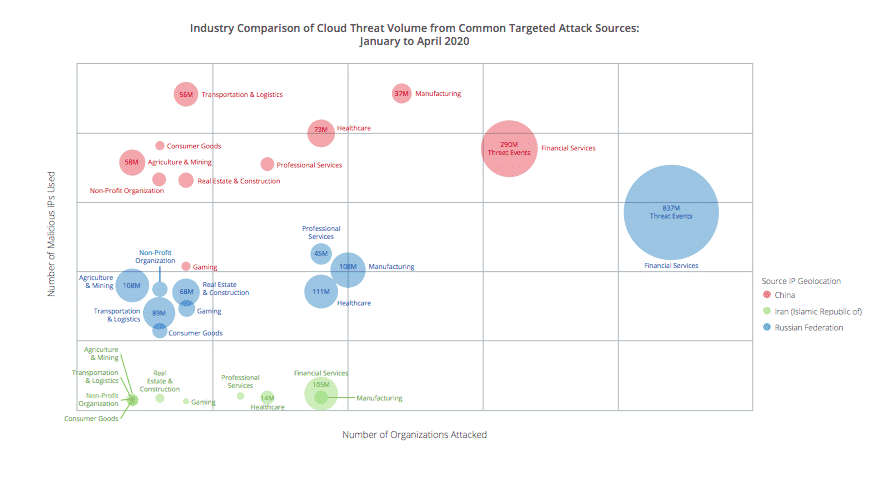 *McAfee Cloud Adoption and Risk Report
*McAfee Cloud Adoption and Risk Report
Healthcare Cybersecurity and Cloud Services
As is evident by McAfee’s report, healthcare cybersecurity is more important than ever. Healthcare organizations are under attack; to prevent healthcare breaches, security measures must be taken to secure protected health information (PHI).
“Threat actors have redoubled their efforts to exploit the distractedness and sudden changes wrought by the world’s response to the pandemic. There are important changes needed to implement new delivery models for security in a distributed, work-from-home environment,” suggests the report.
The researchers further, “However, the data shows that the increased risk of cloud-native threats brought by threat actors targeting cloud services far exceeds the risk brought by changes in behavior by employees simply working in a new, remote location.”
◈ Access Controls. By limiting access to only the data employees need to perform their job function (HIPAA minimum necessary standard), the risk of exploitation is reduced. When all employees have the same access permissions for data, hackers can target any member of an organization, and have access to all of an organization’s data. To implement access controls, each employee must have unique login credentials to enable access to specific data they need as defined by their job role.
◈ Audit Controls. Enables organizations to track access to sensitive data. By implementing unique login credentials for each employee, normal data access patterns can be established for each employee. Not only does this facilitate quick detection of insider breaches, but also alerts administrators to data access that is outside the norm. Many hackers obtain employees login credentials to gain access to sensitive data, when audit controls are implemented, administrators can see that the “employee” is accessing data beyond their normal access patterns, and recognize that the access is in fact by an unauthorized party.
◈ Multi-factor Authentication (MFA). Utilizes multiple unique login credentials to access data. Employees use a username and password in combination with another login credential to access data (i.e., security questions, biometrics, one-time PIN, etc).
◈ Encryption. Masks sensitive information by turning it into a format that can only be read with a decryption key. Encryption is the most effective way to secure sensitive data.
◆ Virtual Private Network (VPN). A service that extends a private network over a public network. When using a VPN to connect to the internet, all data passing through the VPN is encrypted.
◆ Cloud-based Encryption. A service offered by cloud storage providers, cloud-based encryption masks data in transit to and from cloud-based applications.









