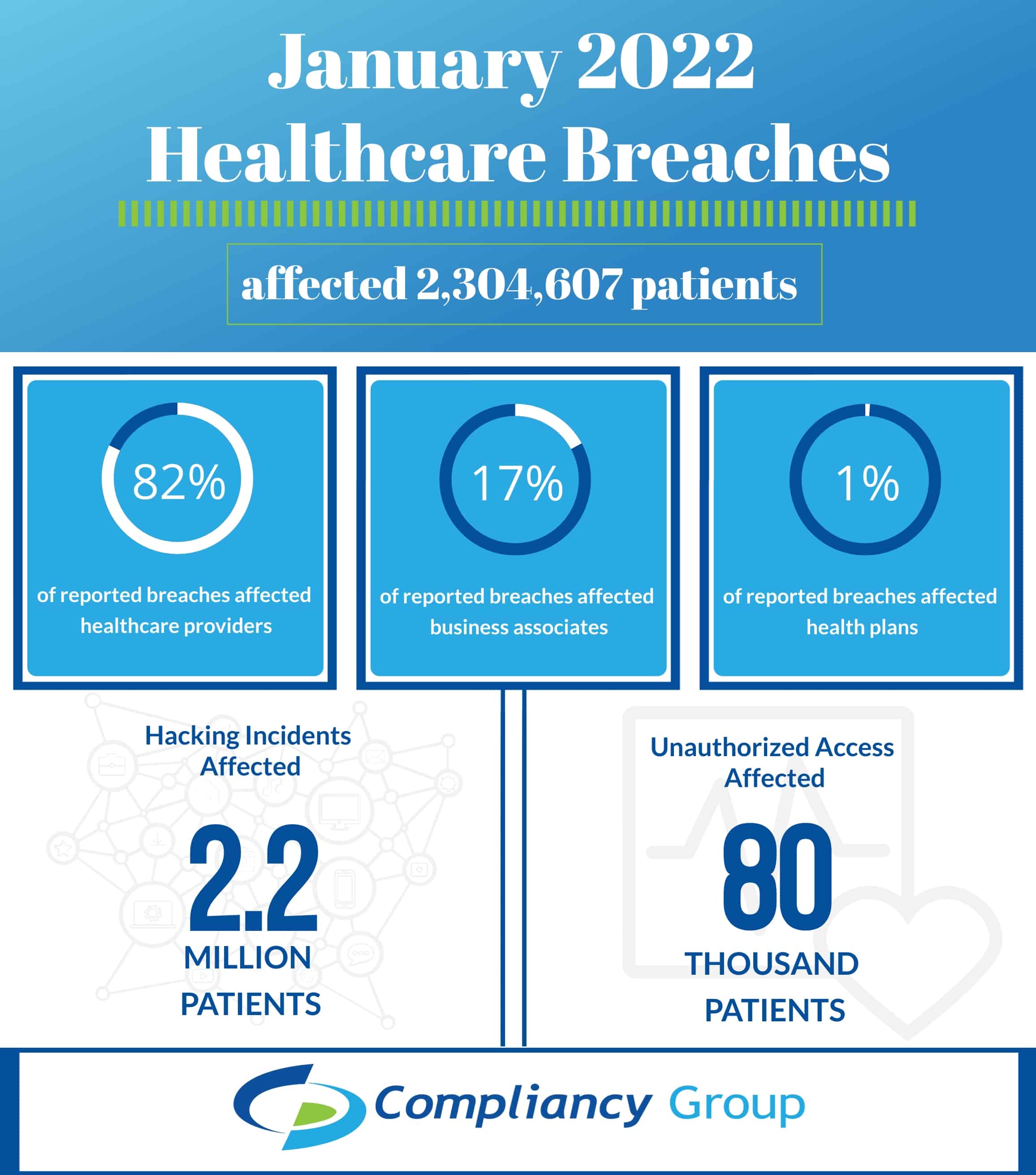
Each month, we review healthcare breaches to determine the leading cause and how the incidents could have been prevented. We do so by examining the Office for Civil Rights (OCR) online breach portal. The OCR publicly posts healthcare breaches that affected 500 or more patients to ensure that all affected patients know their information could have been potentially compromised. In January 2022, there were 50 large-scale breaches reported involving 2,304,607 patients.
Most January 2022 healthcare breaches affected healthcare providers, with 31 incidents. These 31 incidents compromised the protected health information (PHI) of 1,896,191, representing 82.28% of patients affected by January incidents. Business associates reported an additional 13 incidents. Business associate incidents affected 382,585 patients, representing 16.6% of patients affected. Six health plans also reported incidents affecting 25,831 patients and representing 1.12% of affected patients. In January, two types of incidents caused the majority of breaches – hacking incidents and unauthorized access or disclosure of PHI. There was also one incident of PHI theft reported that affected 21,601 patients.
January 2022 Healthcare Breaches and Hacking
It is no surprise that hacking was the leading cause behind January 2022 healthcare breaches. There were 38 hacking incidents reported in January that affected 2,202,550 patients. These 38 incidents represented 95.57% of patients affected by January incidents.
Entities affected by hacking:
- 24 healthcare providers, 1,811,264 patients, 82.23% of patients affected by hacking
- 12 business associates, 255,286 patients, 11.59% of patients affected by hacking
- 2 health plans, 136,000 patients, 6.17% of patients affected by hacking
Types of hacking incidents:
- 11 email hacks, 1,436,220 patients, 65.21% of patients affected by hacking
- 25 network server hacks, 755,941 patients, 34.32% of patients affected by hacking
- 2 “other” hacks, 10,389 patients, 0.47% of patients affected by hacking
How to Prevent Hacking Incidents
As hacking incidents have become the leading cause behind healthcare breaches for several years, it is crucial to minimize your risk of being targeted.
Security Risk Assessments and Remediation
Security risk assessments (SRAs) are vital for security and compliance. The purpose of an SRA is to identify weaknesses and vulnerabilities in your security practices so that you can prepare yourself against potential threats. Once SRAs have been conducted, it is important to create remediation plans to address any identified deficiencies.
Employee Cybersecurity Training
A large portion of hacking incidents stem from phishing emails. This is why employee cybersecurity training is essential to your organization’s overall security posture. Employees should be trained on recognizing phishing attempts, and what to do if they suspect an incident has occurred.
January 2022 Healthcare Breaches and Unauthorized Access or Disclosure
Incidents of unauthorized access or disclosures of PHI can occur in two ways – an authorized employee access PHI inappropriately, or an unauthorized party gains access to PHI. In January 2022, there were 11 incidents of unauthorized access or disclosure of PHI. These incidents affected 80,456 patients, representing 3.49% of patients affected by January incidents.
Entities affected by unauthorized access or disclosure:
- 6 healthcare providers, 74,936 patients, 93.14% of patients affected by unauthorized access or disclosure
- 4 health plans, 4,049 patients, 5.03% of patients affected by unauthorized access or disclosure
- 1 business associate, 1,471 patients, 1.83% of patients affected by unauthorized access or disclosure
Types of unauthorized access or disclosure:
- 1 network server incident, 41,692 patients, 51.82% of patients affected by unauthorized access or disclosure
- 7 paper/films incidents, 29,143 patients, 36.22% of patients affected by unauthorized access or disclosure
- 1 email incident, 7,632 patients, 9.49% of patients affected by unauthorized access or disclosure
- 1 EMR incident, 1,471 patients, 1.83% of patients affected by unauthorized access or disclosure
- 1 desktop computer incident, 518 patients, 0.64% of patients affected by unauthorized access or disclosure
How to Prevent Unauthorized Access or Disclosure
As we mentioned, there are two ways in which unauthorized access or disclosures occur – employee inappropriate access or unauthorized access by another entity.
Policies and Procedures and Employee Training
HIPAA policies and procedures are an essential part of HIPAA compliance as they guide employees on what is appropriate. HIPAA requires employee use and disclosure of PHI to be limited to the minimum necessary required to perform their job functions. Your policies and procedures should dictate this, and employees should be trained on the policies and procedures so that they are aware of their obligations.
User Authentication, Access Controls, and Audit Controls
To ensure adherence to the minimum necessary standard, you must implement user authentication, access controls, and audit controls. User authentication provides unique login credentials for each employee, while access controls enable administrators to designate different PHI access levels using those unique login credentials. Also, based on the implementation of unique login credentials, audit controls track access to data to ensure that PHI is accessed appropriately by each employee.