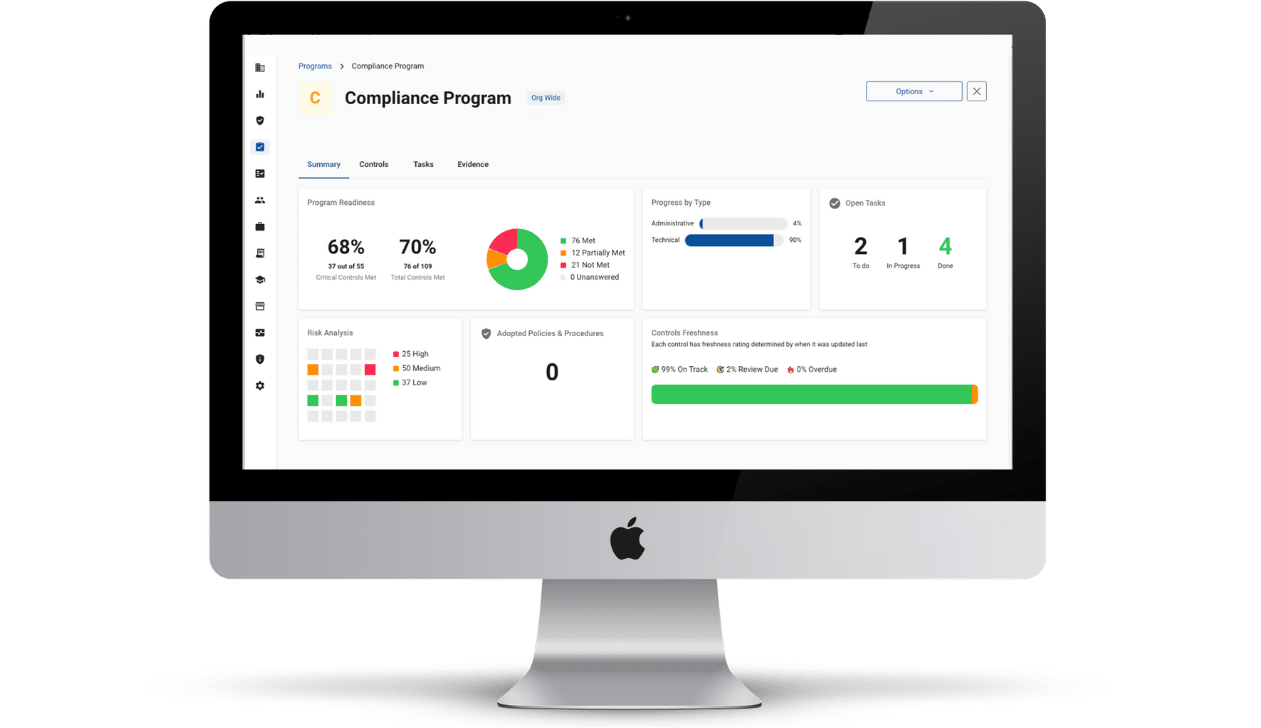
Timberline Billing Service, LLC., a business associate that provides Medicaid reimbursement and billing services to 190 school districts in Iowa, suffered a breach affecting 116,131 patients. More details on the Medicaid billing breach are discussed.
What Caused the Medicaid Billing Breach?

Timberline Billing Service began notifying Iowa school districts that it had suffered a breach. The breach occurred when an unauthorized entity accessed the organization’s network from February 12 to March 4. Upon gaining access to the network, hackers began encrypting some files, while removing others from the organization’s system.
The protected health information (PHI) compromised in the incident included patient names, dates of birth, Medicaid identification number, and related billing information. Some patients’ Social Security numbers were also contained in the exposed files. As a result of the Medicaid billing breach, Timberline Billing Service is offering affected patients credit monitoring and identity protection services.
Timberline Billing Service is also implementing increased security measures including resetting all user passwords, requiring password rotations, upgrading firewalls, and migrating data to a cloud-based storage solution.
In accordance with HIPAA requirements, Timberline Billing Service has notified the Department of Health and Human Services’ (HHS) Office for Civil Rights (OCR) of the breach. Since the breach affected more than 500 patients, the OCR has listed the breach on its breach portal for public display.
How to Protect Your Organization Against a Breach
The best way to protect your organization from succumbing to a breach is by adopting an effective HIPAA compliance program. Through HIPAA compliance, vulnerabilities and threats to your PHI are identified so that you may implement remediation efforts to secure the PHI.
An effective HIPAA compliance program includes:
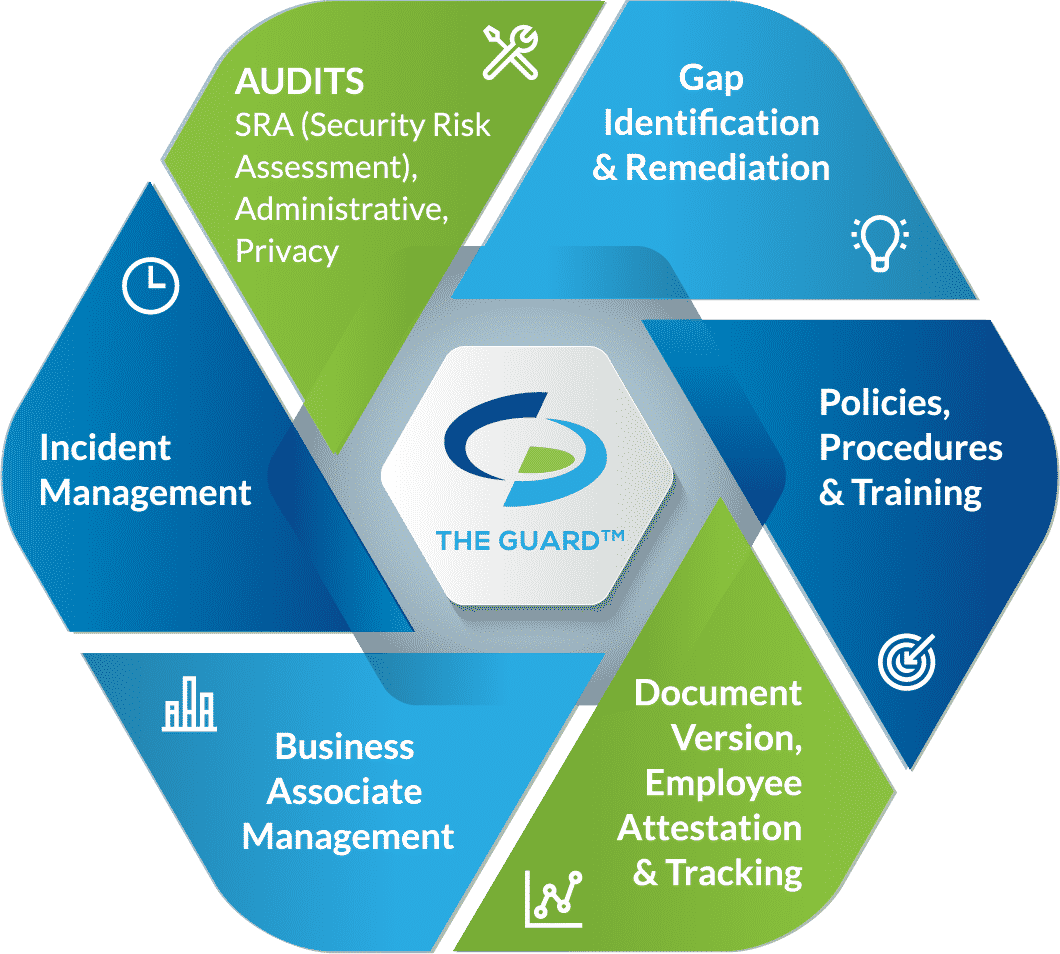
Self-audits. Assesses your organization’s security practices to identify weaknesses in your safeguards. To be HIPAA compliant you must conduct self-audits annually.
Gap identification and remediation. Allows you to increase your security by addressing gaps in your safeguards.
Policies and procedures. Dictates the proper uses and disclosures of PHI, how you protect PHI, and steps to take to report a breach.
Business associate management. Assesses your business associates’ HIPAA compliance, and provides you with business associate agreements to comply with HIPAA standards.
Employee training. To ensure that employees are aware of their responsibilities to HIPAA, they must be trained annually.
Incident response. Should your organization fall victim to a breach, you must report it to the HHS OCR, affected patients, and in some instances the media.