What is Healthcare Compliance Software?
HIPAA compliance is multifaceted, navigating HIPAA compliance can be difficult to do on your own. That’s where healthcare compliance software comes in. Healthcare compliance software allows organizations working in healthcare to track and manage their HIPAA compliance.
Confidentiality, Integrity, and Availability
HIPAA compliance requires organizations working with protected health information (PHI) to ensure its confidentiality, integrity, and availability.
◈ Confidentiality. PHI collected on patients holds a wealth of information. When PHI falls into the wrong hands, it can be used to commit identity theft or fraud. Organizations working with PHI have an obligation to ensure the confidentiality of PHI, protecting it against unauthorized individuals.
◈ Integrity. PHI must also be protected against corruption. As such, healthcare organizations must implement safeguards to prevent individuals from altering PHI without authorization.
◈ Availability. To ensure quality of service, PHI must be readily available. This includes having access to PHI in the event of an emergency or natural disaster.
Reasonably Appropriate
Within the HIPAA regulation, it states that organizations must implement “reasonably appropriate” safeguards to secure PHI. HIPAA does not specify what these safeguards must be as the law was written intentionally vague. This is because the regulation applies to a variety of types and sizes of organizations.
HIPAA Safeguards
HIPAA states that organizations must implement “reasonably appropriate” safeguards to secure PHI. Implementing safeguards enables the confidentiality, integrity, and availability of PHI. Safeguards include administrative, physical, and technical protections.
◈ Administrative. HIPAA requires PHI to be used and disclosed in accordance with the minimum necessary standard. The minimum necessary standard states that PHI should only be used and disclosed for a specific purpose. As such, organizations must implement administrative safeguards to control and track access to PHI.
◆ Unique Login Credentials. Each employee must have unique login credentials to access systems containing PHI. Giving users unique login credentials allows administrators to designate different levels of access to PHI based on an employee’s job function. Unique login credentials also allows administrators to track access to PHI, and determine normal access patterns for each employee to prevent and detect insider breaches.
◆ User Authentication. To ensure that users are who they appear to be, organizations should implement multi-factor authentication (MFA) for user authentication. MFA utilizes multiple login credentials such as username and password in combination with another unique identifier (i.e. security questions, biometrics, one time PIN, etc.) to confirm a users’ identity.
◆ Access Controls. Enabled through the use of unique login credentials, access controls designate different levels of access to PHI based on a user’s job role. Access controls ensure adherence to the minimum necessary standard as users only have access to the data that they need to perform their job functions.
◆ Audit Logs. To ensure that authorized users do not access PHI excessively, and to quickly detect unauthorized access to PHI, it is essential to keep audit logs. Audit logs track access to PHI. Tracking authorized access to PHI establishes normal access patterns for each user, enabling quick detection of insider breaches. Audit logs also enable the quick detection of unauthorized access to PHI.
◈ Physical. Physical safeguards refer to securing PHI at an organization’s physical location. This includes installing an alarm system and locking areas in which PHI is stored.
◈ Technical. To ensure that electronic protected health information (ePHI) – PHI stored in an electronic format – is secure, organizations must implement technical safeguards. This includes encrypting data, installing firewalls and antivirus software, etc.
Healthcare Compliance Software: Good Faith Effort
Since HIPAA compliance is ongoing, there is no such thing as a HIPAA certification. All an organization can do is prove their “good faith effort” towards HIPAA compliance. For an organization to prove their “good faith effort” they need to have documentation that shows that they have implemented an effective compliance program. Utilizing a healthcare compliance software allows organizations to implement a fully documented HIPAA compliance program.
Compliancy Group’s Healthcare Compliance Software
Compliancy Group’s healthcare compliance software allows organizations to implement an effective compliance program. Our healthcare compliance software enables organizations to implement, document, and maintain a compliance program that covers the full HIPAA requirements.
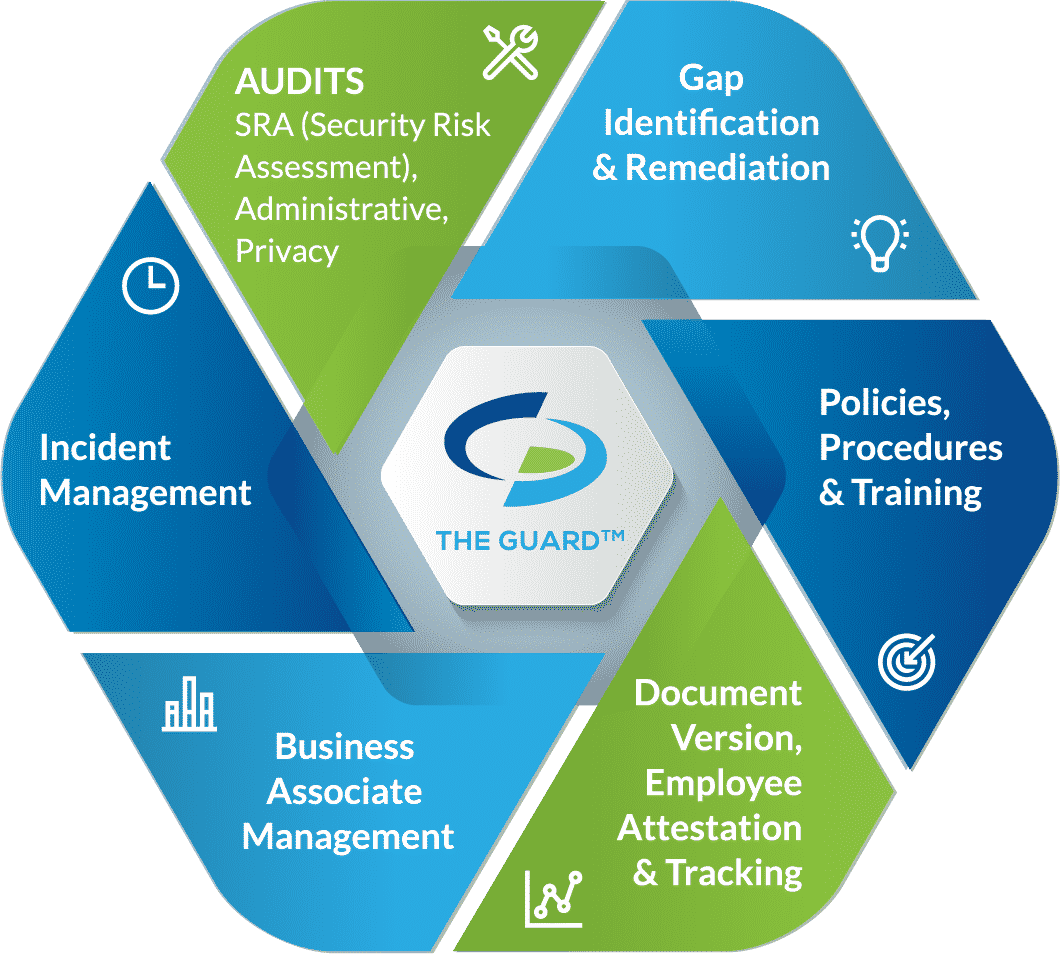
◈ Risk Assessments. Covered entities are required to conduct six self-audits annually, while business associates and MSPs must complete five. Completing self-audits measures administrative, physical, and technical safeguards against HIPAA standards.
◈ Gap Identification and Remediation. Upon completion of self-audits, gaps in an organization’s safeguards are identified. To be HIPAA compliant, gaps must be addressed with remediation plans. Remediation efforts close gaps so that safeguards are adequately securing PHI.
◈ Policies and Procedures. A major component of HIPAA is illustrating compliance through documentation. As such, organizations must have customized policies and procedures dictating how they plan to adhere to the HIPAA Security, Privacy, and Breach Notifications Rules.
◈ Employee Training. To ensure that employees properly use and disclose PHI, they must be trained annually. HIPAA training should include HIPAA basics, their organization’s policies and procedures, proper use of social media, and cybersecurity.
◈ Business Associate Management. Before working with a vendor, it is essential to assess their safeguards. Vendors (business associates) are required to be HIPAA compliant to work with healthcare clients. They must also be willing to sign a business associate agreement (BAA). A BAA must be signed before it is permitted to share PHI with the business associate. A BAA is a legal document that dictates the safeguards the business associate is required to have in place, it also requires each party to be responsible for maintaining their compliance.
◈ Incident Response. If an organization experiences a breach, they have an obligation to report it. Additionally, employees must have a means to report breaches anonymously. Our HIPAA software allows this, while also allowing administrators to track reported incidents.